Many men in Kenya hardly seek treatment due to stigma, lack of awareness, or limited access to specialised care.
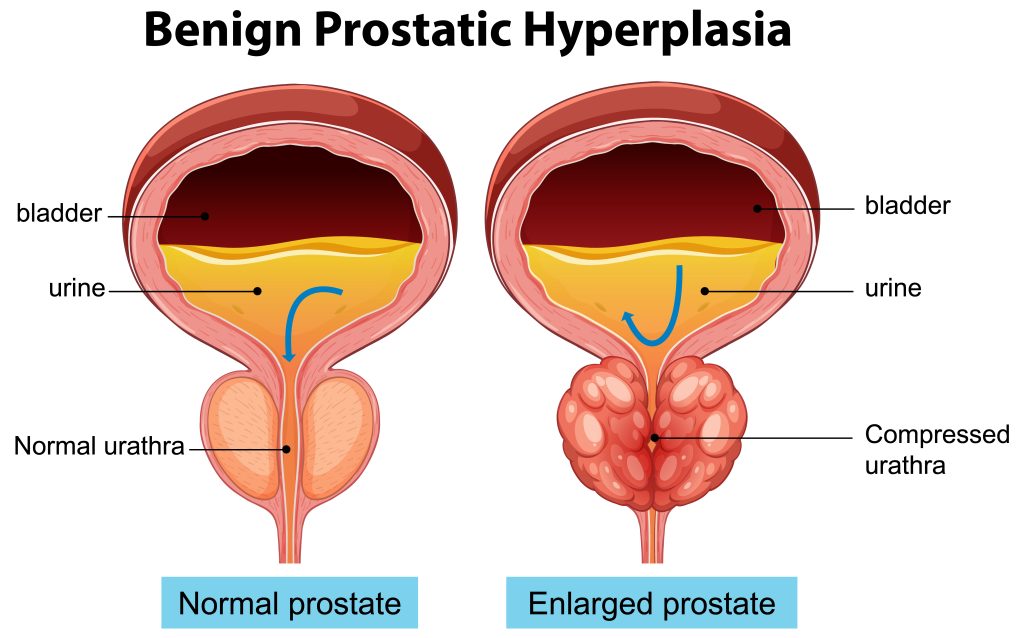
As men age, the prostate gland naturally grows, but for many, that growth can lead to uncomfortable and sometimes serious urinary symptoms. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland located just below the bladder. Its main job is to help produce the fluid that carries sperm, commonly known as semen.
When it gets too big, it can press against the urethra – the tube that carries urine out, and that’s when problems begin.
Prostate enlargement, medically known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), affects millions of men, and a study published in the American Urology Association Journal notes that Black men and Hispanic/Latino men are 41% more likely to develop BPH than white men. Apart from age, other additional risk factors for prostate enlargement include African heritage and family history.
Common signs of BPH
- A weak or interrupted urine stream
- Difficulty starting urination
- A frequent or urgent need to urinate, especially at night
- A sensation of incomplete bladder emptying
- Dribbling at the end of urination
While these symptoms can be frustrating, they typically develop gradually and are often manageable, especially when addressed early. However, if left untreated, persistent symptoms of prostate enlargement can lead to recurrent urinary tract infections due to retained urine, and in some cases, the presence of blood in the urine or damage to the kidneys, leading to bladder stones.
The diagnostic process for prostate enlargement begins with a thorough clinical evaluation, where a healthcare provider examines the patient and takes a detailed medical history.
This initial step is crucial in identifying symptoms and ruling out other conditions. Following the clinical assessment, patients are typically referred for laboratory tests and an ultrasound scan, which help confirm the diagnosis.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, doctors assess the severity of the condition to determine the most appropriate treatment plan. The treatment options vary depending on the patient’s symptoms, prostate size, and overall health.
Fortunately, there is a wide range of treatment options, categorised into three main areas: lifestyle modifications, medical therapy, and surgical intervention.
Prostate Enlargement Treatment
- Lifestyle modifications
- Medical therapy
- Surgical intervention
Lifestyle changes may include reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, limiting fluid consumption before bedtime, and adopting healthier eating habits.
While many men with prostate enlargement respond well to medication and lifestyle changes, there are cases where surgery becomes necessary. Such include those who do not respond to medical therapy, those facing serious complications, like recurrent urinary tract infections, those who pass blood in their urine, and individuals suffering from urine retention. Surgery is also advised for men who develop bladder stones or face the risk of kidney failure linked to the condition.
Myths and misconceptions continue to cloud public understanding of BPH, resulting in reluctance to seek medical help.
According to the Kenya Association of Urological Surgeons (KAUS), BPH is the most common urological condition in men over 50. Yet less than 40 per cent of symptomatic men in Kenya seek treatment due to stigma, lack of awareness, or limited access to specialised care.
Though BPH is not cancer, some symptoms overlap with prostate cancer, which makes it essential to consult a doctor when problems arise. A simple physical exam, along with a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, can help determine the cause.
Prostate enlargement is a natural part of ageing for many men, and early diagnosis and treatment can make all the difference.
Undescended Testes: Causes, risks, and why early surgery matters
Undescended testes may seem minor at first, but without timely treatment, they can lead to fertility challenges, hormonal issues, and even cancer later in life. Early detection and surgical correction give your child the best chance at a healthy future.